Fungal infections in rabbits are caused by fungi that invade and grow on the skin, fur, or internal tissues. These infections can lead to symptoms such as itching, hair loss, and skin lesions, and can sometimes cause more serious health problems if left untreated.
Rabbits, cherished for their soft fur and gentle demeanor, can sometimes fall prey to fungal infections. These infections can cause a variety of health issues, affecting the skin, fur, and overall well-being of our furry friends. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the reasons behind fungal infections in rabbits, examine effective treatments, discuss prevention strategies, and provide answers to frequently asked questions.
Common Types of Fungal Infections in Rabbits:
- Ringworm (Dermatophytosis):
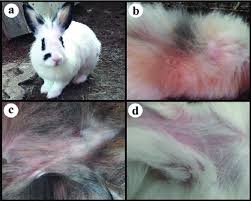
- Caused by fungi such as Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Microsporum canis, ringworm manifests as circular patches of hair loss, redness, and scaling.
- Yeast Infections:
- Candida albicans can cause yeast infections, particularly in the ears and digestive tract, leading to symptoms like itching, discharge, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Aspergillosis:
- Caused by Aspergillus species, this fungal infection primarily affects the respiratory system, leading to respiratory distress, nasal discharge, and lethargy.
Reasons for Fungal Infections in Rabbits:
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the rabbit’s living environment can lead to fungal growth, increasing the risk of infection.
- High Humidity and Warmth: Fungi thrive in warm and humid conditions, making rabbits more susceptible to infections in such environments.
- Weakened Immune System: Rabbits with compromised immune systems due to illness, stress, or poor nutrition are more prone to fungal infections.
Clinical Signs of Fungal Infections in Rabbits:
Ringworm (Dermatophytosis):
- Circular patches of hair loss
- Redness and scaling of the skin
- Itching and irritation
- Crusty or flaky skin lesions
Yeast Infections:
- Itching and scratching, particularly around the ears
- Discharge from the ears
- Redness and inflammation
- Gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea or bloating
Aspergillosis
- Respiratory distress
- Nasal discharge
- Sneezing and coughing
- Lethargy and decreased appetite
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections in Rabbits:
- Medication:
Veterinarians may prescribe antifungal medications such as topical creams, oral medications, or injections to treat fungal infections. These treatments help eliminate the fungi and alleviate symptoms.

- Environmental Control:
Regular cleaning and disinfection of the rabbit’s living area, bedding, and accessories are crucial to prevent reinfection and control the spread of fungi.
- Supportive Care:
Maintaining proper hygiene, providing a balanced diet, and ensuring a stress-free environment can support the rabbit’s recovery and overall health.
- For eye infections in Cat and dogs [CLICK HERE]
Prevention Strategies:
- Regular Grooming:
Frequent grooming helps remove loose fur and debris, reducing the risk of fungal infections. It’s also an opportunity to check for early signs of infection.
- Environmental Management:
Keeping the rabbit’s habitat clean and dry, and controlling humidity levels, can create an environment less conducive to fungal growth.
- Proper Nutrition:
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports the rabbit’s immune system, making them less susceptible to infections.

Conclusion:
Fungal infections can pose a significant health risk to rabbits, but with proper understanding, treatment, and prevention, pet owners can effectively manage these issues and ensure the health and well-being of their rabbits. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and consulting with a veterinarian when necessary, rabbit owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from fungal infections. Remember, a healthy rabbit is a happy rabbit!
FAQs About Fungal Infections in Rabbits:
Q1: Can fungal infections in rabbits affect other pets or humans?
A1: Yes, some fungal infections, such as ringworm, are zoonotic and can spread to other pets and humans. It’s important to handle infected rabbits with care and practice good hygiene.
Q2: How can I tell if my rabbit has a fungal infection?
A2: Symptoms of fungal infections in rabbits include hair loss, itching, redness, scaling, and in severe cases, respiratory issues or gastrointestinal disturbances. A veterinary diagnosis is essential for proper treatment.
Q3: Are there home remedies for treating fungal infections in rabbits?
A3: While some home remedies may provide temporary relief, it’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Self-treatment can sometimes worsen the condition.
Q4: How long does it take for a rabbit to recover from a fungal infection?
A4: Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the infection and the treatment used. With proper veterinary care, most fungal infections can be successfully treated within a few weeks.
Q5: Can fungal infections be prevented in rabbits?
A5: Yes, maintaining good hygiene, providing a balanced diet, and keeping the rabbit’s environment clean and dry can significantly reduce the risk of fungal infections.

