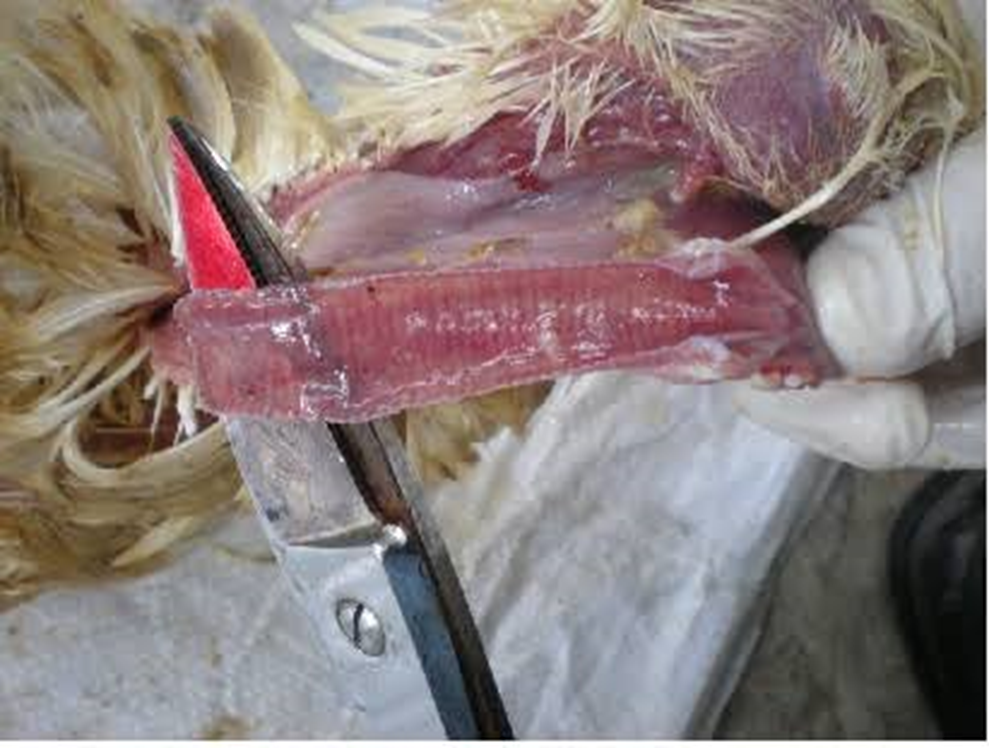
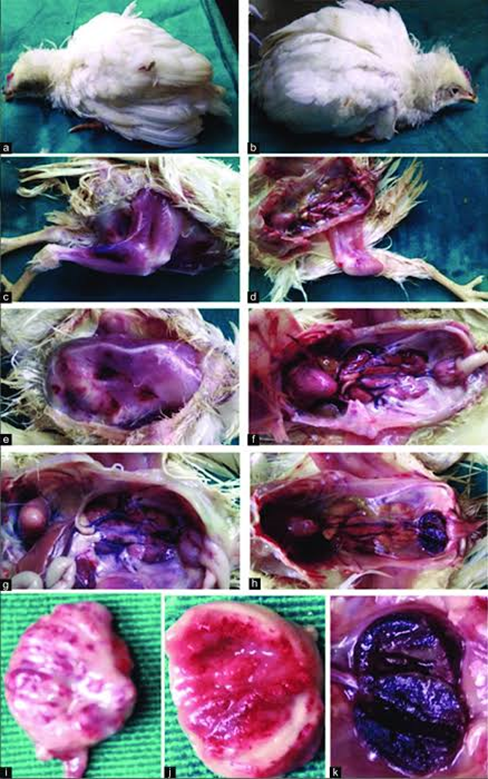
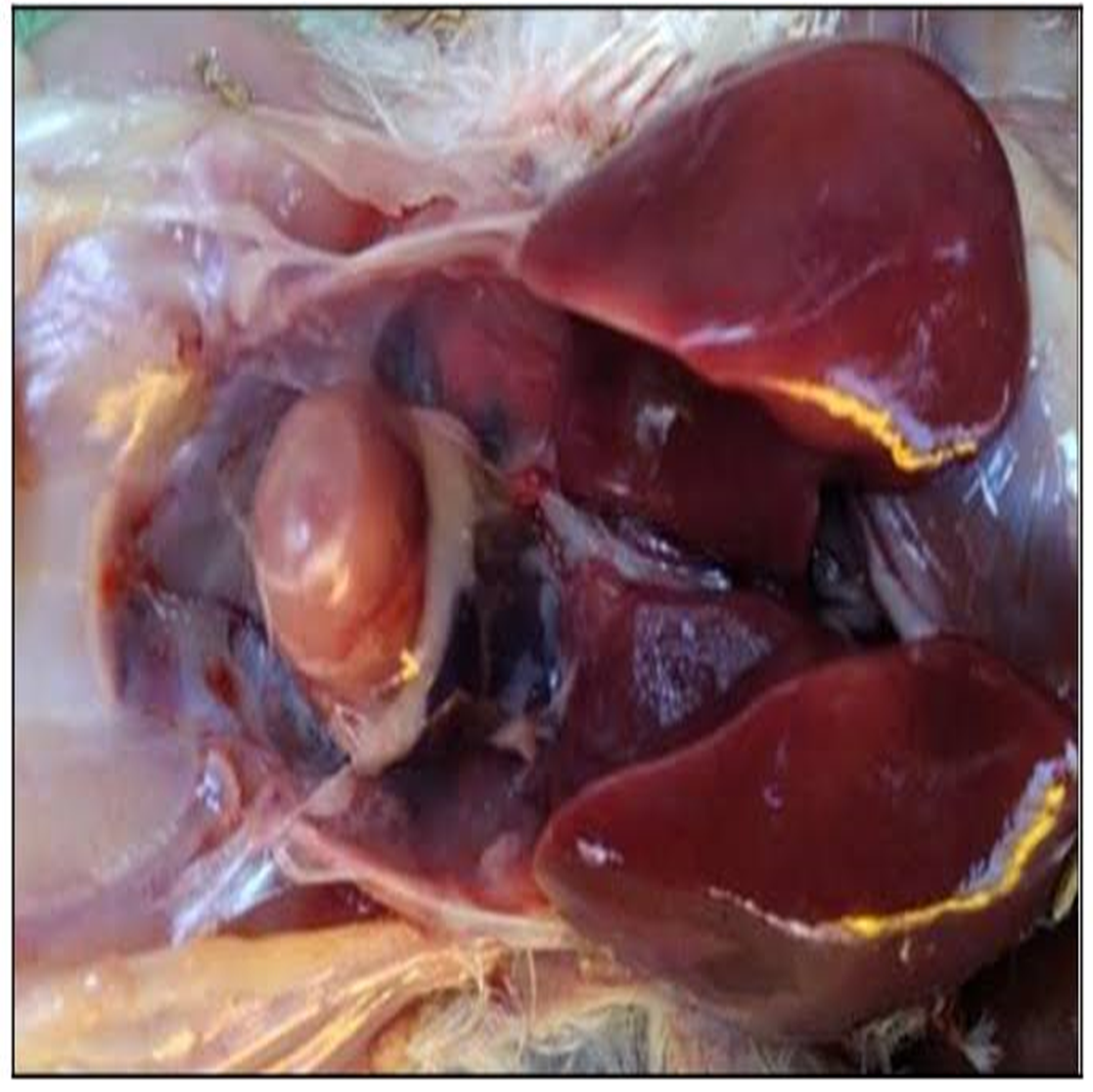
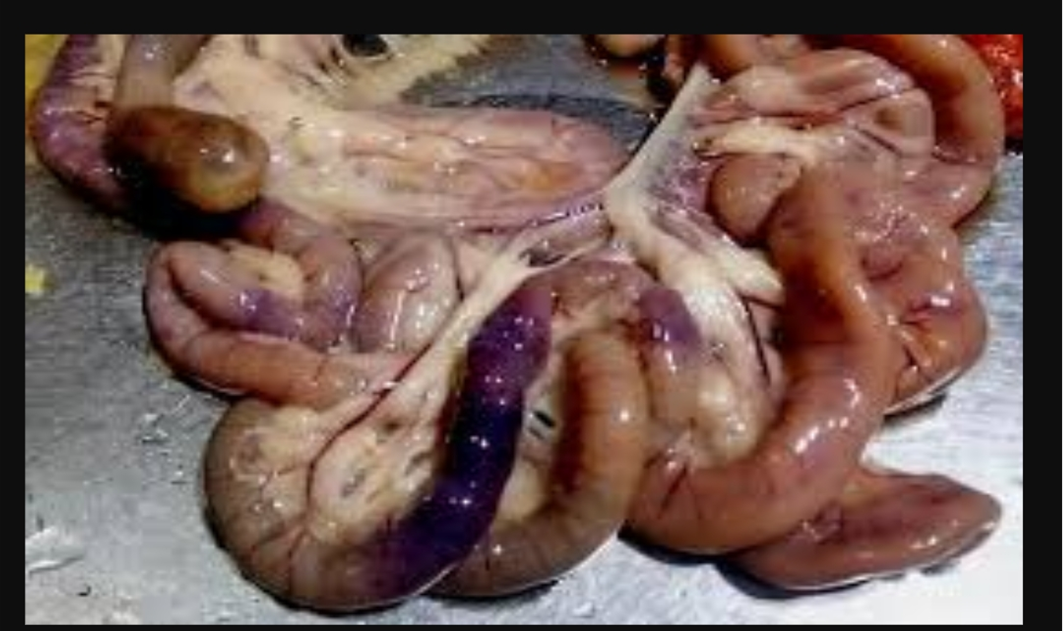
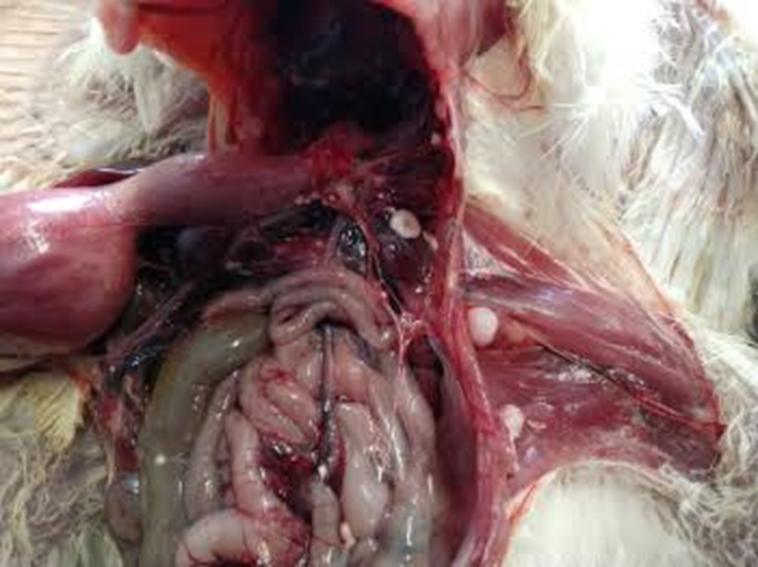
Sanitization in Poultry Disease Management
Poultry farming is a critical sector in the food industry, providing a significant portion of the world’s meat supply. However, the industry faces numerous challenges, particularly in disease management. Sanitization in Poultry plays a pivotal role in preventing and controlling diseases within poultry flocks. Importance of Sanitization in Poultry Disease Management: Sanitation in poultry farming … Read more